Is there a difference between the consumers who use a neobank like Chime or Dave versus those who choose a digital-only bank like Ally Bank or a Marcus?
There is, and the differences are critical to understand if a bank or credit union is revamping its online banking services or mobile app, or is considering a national digital niche bank strategy.
Traditional institutions attempting to compete with digital-only banks (sometimes referred to as direct banks), need to understand how the user profiles of digital-only banks differ from those of neobanks. 27% of American banking customers use an digital provider of some type for at least part of their financial needs, according to J.D. Power.

The Financial Brand Forum Kicks Off May 20th
Explore the big ideas, new innovations and latest trends reshaping banking at The Financial Brand Forum. Will you be there? Don't get left behind.
Read More about The Financial Brand Forum Kicks Off May 20th

Industry Cloud for Banking from PwC
PwC’s Industry Cloud for Banking applies our deep industry knowledge to your specific business needs
Comparing Customers of Digital-Only Banks and Neobanks
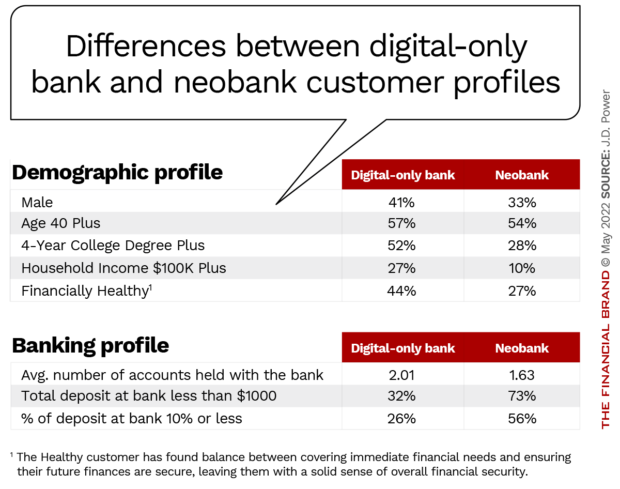
Research from the firm reveals some sharp distinctions between why consumers engage with one type of provider over the other. Digital-only banks and neobanks often get lumped together but J.D. Power’s research points to some striking differences between their typical customers.
A Key Digital Bank-Neobank Difference:
Neobanks tend to appeal to fee-sensitive customers, while digital-only banks tend to attract people sensitive to interest rates.
In its 2022 U.S. Direct Banking Satisfaction Study and new companion research on neobank satisfaction, the research firm found that neobank customers are more likely to be women, have less education, and lower income than customers of digital-only banks. They tend to run lower balances and to own fewer financial products overall.
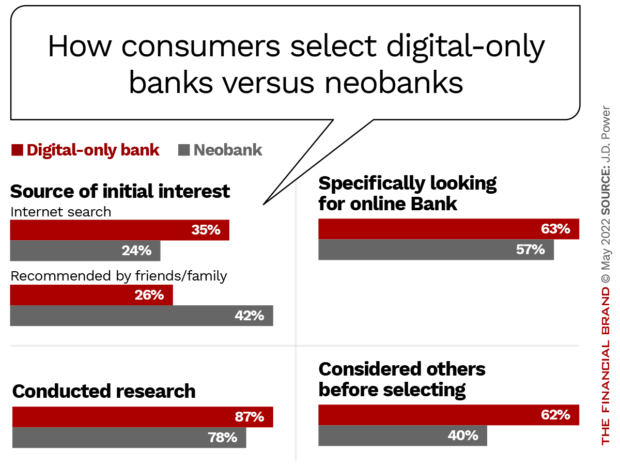
In addition, they generally decide where to put their money differently than do customers of digital-only banks. J.D. Power found that neobank users tend to rely on recommendations from friends and family, rather than researching the options themselves. By contrast, users of digital-only banks work the internet to find the deal and digital institution that best suits their needs.
As a result, users of digital-only banks tend to give more of their business to their online provider, while neobank users are often just giving the neobank a tryout. They lack full commitment and they often maintain a checking account with mainstream banks or credit unions rather than commit to the fintech provider.
Paul McAdam, Senior Director of Banking and Payments Intelligence at J.D. Power, explains in an interview with The Financial Brand that the origins of the two types of digital providers account for some of the differences between digital-only banks and neobanks. Digital-only banks as a concept go back a couple of decades, and a good part of their growth comes from being able to offer higher rates on deposits because they have no branch system to maintain. (Ally Bank, for example, was launched in 2004.)
Neobanks, on the other hand, may at times promote deposit rates, but more often they compete on the basis of offering low- or no-fee options and other services for people with limited resources. Early wage access, no-fee overdraft service and other product features that can assist people with little excess cash all help neobanks appeal to their core market.
Read More:
- 5 Popular Fintech App Features Banks Should Add to Mobile Banking
- The World’s Biggest List of Digital Banks
- 5 Mobile Banking App Pain Points That Must Be Eliminated
- Digital Bank & Fintech Slogans: 200+ Taglines from Around the World
It’s Not a Simple ‘Us Versus Them’ Challenge
In a sense, there’s a three-sided struggle going on.
“Neobanks are today’s new market entrants, capturing transaction (checking) account market share from direct [digital-only] banks and traditional players,” states J.D. Power.
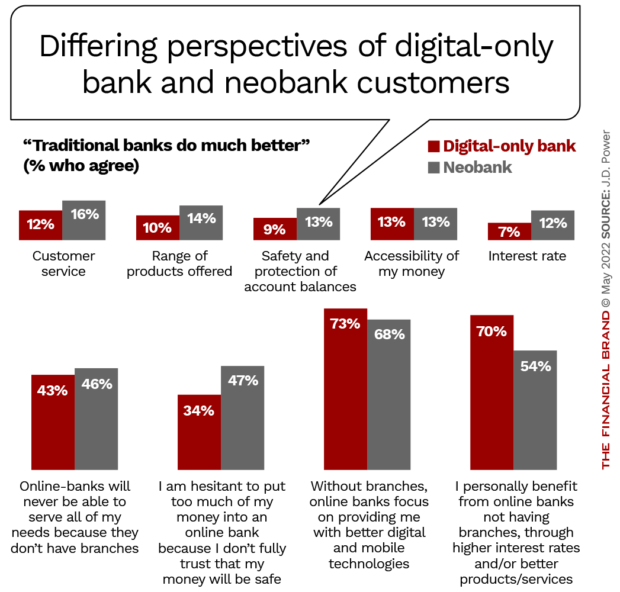
A surprising factor in the digital-mix is the branch. J.D. Power found that 43% of digital-only bank users and 46% of neobank users don’t believe that their providers can serve all of their financial needs, in part because they lack branches.
Customer loyalty doesn’t guarantee that people will stick to either institution. According to J.D. Power, even among users who give providers strong overall satisfaction ratings of 700 points or more (out of 1,000), neobank customers were less likely to say that they would definitely not switch to another provider. And among neobank customers with checking account satisfaction ratings of over 700, they were much more likely to switch because they preferred an institution with branches.
The research also found that, in spite of going for the newest providers, neobank customers maintain a more favorable view of traditional banks than do direct bank users.
Read More: The Most Popular Digital-Only Banks in the World

How Banks and Credit Unions Can Compete Better
A key lesson of the research is that neobanks are drawing consumers who are younger, less financially secure and more concerned about bank fees than other generations. But there’s a corollary to that. Those consumers are the next generation of primary customers and now is the time to begin appealing to them across the board.
McAdam had several recommendations:
1. Reconsider where you are making your money.
Pricing philosophy differs among traditional banking institutions, digital-only institutions and neobanks at present. However, McAdam says that the elimination or easing of overdraft fees at a growing number of mainstream players illustrates a coming together of attitudes towards fees. He says that as traditional players adopt such measures —some of them adding features like early wage access — this will push other traditional institutions to keep up.
“This will be what is required for institutions to continue to get their fair share of younger customers,” says McAdam. Neobanks are gradually killing fees.
While this will be costly, McAdam says the price must be seen in the context of what additional services those customers will need that will allow institutions to earn more revenue. “These people will need credit cards, they’ll need car loans and more,” says McAdam.
2. Start thinking about what can be added to accounts to make money.
The revenue-generating abilities of checking and other core accounts may not come from service or penalty fees, increasingly, but from other services that can be hooked onto the accounts for a subscription fee. McAdam says the strong affinity younger people have for subscriptions of many kinds makes a natural tie in to a financial account, from which they would pay for those services.
3. Start moving to emulate neobanks’ personalization moves.
A big plus for neobanks is consumers’ perception that many of their services are tailored to their needs and circumstances. Fees are a key element of this — consumers told J.D. Power that they wanted help to avoid fees, including warnings before they incur them.
McAdam says that a model banks and credit unions can review for ideas are the ways that the three major credit bureaus have built package accounts around access to credit reports and related services.
4. Stop listening to anti-branch pundits.
Along with other steps to appeal to younger consumers, their clear desire that some physical locations supplement digital service can’t be ignored, McAdam says.
“Branch visits are declining, we all know that,” says McAdam. However, while they don’t transact at branches, young people do visit branches to open an account or to get advice.” Their desire for branches has been seen in multiple retail banking studies by J.D. Power, he says.
Read More: This Small Bank Says Its Brand Will Succeed Where Chase Failed

Send the Right Offers to the Right Consumers
Achieve a better return on your marketing investment. Leverage behavioral data and analytics to target the right customers with the best possible offers.
Read More about Send the Right Offers to the Right Consumers

Instant Messaging. Instant Impact.
Connect with your customers and provide lightning-fast support as effortlessly as texting friends. Two-way SMS text messaging is no longer optional.
Service Quality Is a Major Sore Point
Both the direct bank satisfaction study and the neobank study focused on the issue of service quality, something that many digital-only institutions and neobanks struggle with.
“The biggest driver of the differences in the study was customer service,” says McAdam. He explains that the ability to get a human being on the phone, especially if there is a problem to be worked out, ranks higher than other factors. Dissatisfaction with a company because it was hard to get help often drove down customers’ ratings of their providers.
It's Not All About Digital:
A factor J.D. Power found to be key to customers of both digital-only banks and neobanks is service quality —specifically, service delivered by fellow humans.
Only 61% of digital-only bank users say they find it convenient to get through to customer service and only 47% — less than half — of neobank users said so. And neobank users report that communications and interactions with their provider are consistent only 35% of the time.
In fact, in the direct banking satisfaction study, the ranking of companies by customer satisfaction, on a 1,000 point scale, saw Charles Schwab Bank (715), Discover Bank (715), Ally Bank (709) and Capital One (703) leading the field, among checking providers. These players were ahead of other players like Varo Bank (647), a relative newcomer that has ridden a strong wave of publicity because it went from a neobank to a federally chartered institution.
The issue of customer service quality also comes up when the direct banking study is compared with a new one about neobanks. In the study of digital-only banks, among consumers with checking service from those institutions, the average customer satisfaction rating came to 701 out of 1,000. By contrast, among consumers with checking service from neobanks, the average customer satisfaction rating came to only 630, says McAdam.