Keeping pace with the changing needs of today’s financial services customer is more difficult than ever, with new technologies, personalized product offerings and increasing competition gaining momentum. In the past, many traditional banking organizations looked at fintech start-ups as more of a nuisance than a threat. Today, many are viewing these non-traditional providers as a threat as well as either a partner or potential acquisition.
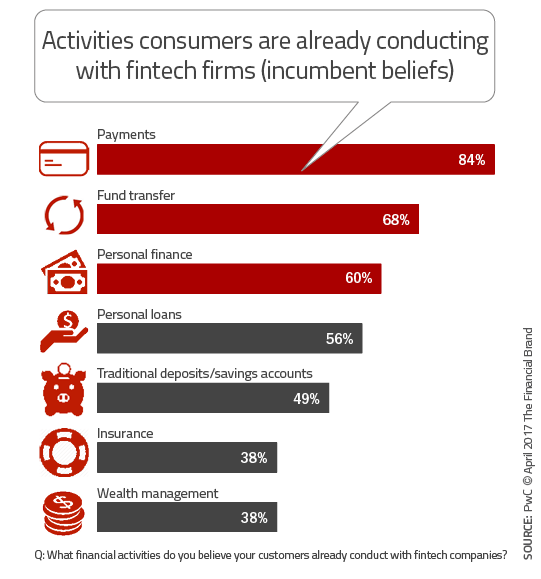
In its latest Global Fintech Report, PwC found that 88% of legacy banking organizations fear losing revenue to financial technology companies in areas such as payments, money transfers and personal loans. The amount of business at risk has grown to an estimated 24% of revenues.
In related DeNovo’s research from PwC, it was found that 30% of consumers plan to increase their usage of nontraditional financial services providers, with only 39% planning to continue using solely traditional service organizations. This is an additional wake-up call to legacy organizations to determine how they will retain the key components of an existing banking relationship.
In response to this threat, 82% of traditional financial organizations stated a plan to increase collaboration with fintech companies in the next three to five years. Similarly, almost 50% of financial services firms are planning to acquire fintech startups over the same period.
“Mainstream financial institutions are rapidly embracing the disruptive nature of fintech and forging partnerships in efforts to sharpen operational efficiency and respond to customer demands for more innovative services,” PwC says in its report. In fact, funding of fintech startups has increased at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 41% over the last four years, with over US$40 billion in cumulative investment, according to PwC’s DeNovo platform.

Navigating Credit Card Issuing in an Uncertain Economic Environment
Build a modern credit card strategy that balances profitability and risk, adopts the latest technology and delivers the customization that cardholders demand.
Read More about Navigating Credit Card Issuing in an Uncertain Economic Environment

Industry Cloud for Banking from PwC
PwC’s Industry Cloud for Banking applies our deep industry knowledge to your specific business needs
Collaborating for a Better Customer Experience
Bottom line, fintech firms and financial innovation in general are changing the financial services ecosystem, redrawing the lines of the financial services industry and the transforming the ways consumers and businesses manage their finances. PwC states: “Fintech startups don’t just need capital, they need customers. At the same time, incumbents need new approaches to drive change and deliver innovation.”
Fintech startups realize that it takes more than a great solution to attract a scalable customer base. To reach beyond early adopters and the tech-savvy takes massive amounts of capital for promotion and product support. Partnering with an established banking organization who will support the expansion of users among their client base seems like a logical means to an end.
Alternatively, legacy banking organizations, struggle to keep up with consumer expectations. Size, organizational structure (silos) and even traditional leadership styles hamper the ability to deliver the new digital solutions consumers receive from other industries. Partnering with a fintech startup alleviates some of these issues, allowing the established organization an opportunity to keep pace with marketplace demands.
Fintech collaboration is not about grabbing for the ‘next shiny object’ — it’s about intuitive product design, ease of use, and 24/7 accessibility. According to PwC, “Embracing fintech is as much about different ways of working and problem-solving as it is about deploying new technology.”
Partnering with fintech companies is up from 32% in 2016 to 45% this year on average, but large discrepancies exist between different countries. For instance, financial institutions in Germany were the most likely to currently have fintech partnerships (70%), with only 14% of organizations in South Korea having this form of collaboration. (53% of US banks had fintech partnerships with 43% of UK banks having the same).
The PwC survey also highlights how innovation is coming from beyond traditional banking and fintech companies. New players that are impacting the industry include tech companies (Google, Apple, Samsung), e-retailers (Amazon, Alibaba), and social media platforms (Facebook, SnapChat).
Focus on New Technologies
The ‘fintech advantage’ has usually been driven by the ability to leverage new technologies and delivery channels. Using advanced analytics, big data and real-time digital delivery, fintech firms have found an Achilles heel in the traditional banking process. To succeed, incumbent firms must concentrate on these same technologies to provide a better consumer experience.
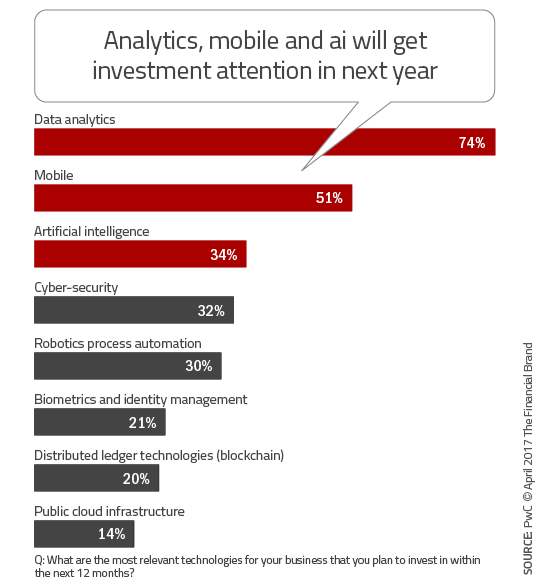
PwC found that most traditional financial institutions are concentrating on updating their legacy systems, with a strong focus on data analytics, mobile technology the beginnings of an artificial intelligence (AI) strategy. In a high stakes game of leap frog, while most incumbents are focusing on consolidating and managing data and to offer personalized digital experiences, fintech firms have moved to the next level, focusing on technologies such as blockchain, advanced AI strategies and biometric authentication.
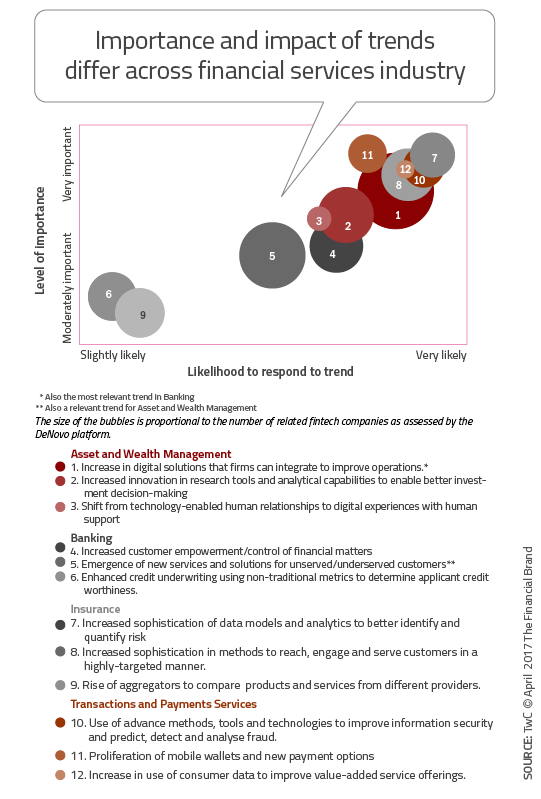
PwC developed a matrix of the important trends in the Banking, Asset and Wealth Management, Insurance and Transactions and Payments Services industries and plotted the importance of each trend against the likelihood of a response to each trend. In the illustration, the size of the ‘bubble’ is related to the number of firms competing in each trend.
Innovation From Within
Globally, 77% of respondents noted that they expect to increase internal innovation efforts over the next three to five years. This is encouraging, and can occur in a variety of ways according to the research, including adopting newer technologies such as Artificial Intelligence (AI) or blockchain, or changing the cultural environment to one that fosters innovation.
Unfortunately many current innovation initiatives seem to be hampered by the same challenges that are driving fintech collaboration with actual outcomes being patchy at best. “For many customers and clients, basic products and services look and cost much the same as they did before,” states PwC. “To succeed, legacy organizations will need to disrupt their own operations or processes, which will introduce culture and mindset challenges.”
Building a Strategy for the Future
PwC stresses that incumbent organizations need to revisit long-standing assumptions regarding competitive strengths, efficiency and effectiveness of current (and future) strategies, consumer expectations of their organization, the likely competitive landscape, and how these might be changing. These same organizations must become much more familiar with new digital technologies and the potential impact on traditional business models.
According to PwC, “There are multiple challenges in incorporating innovation into organizations, including aligning innovation with strategic priorities, building capabilities to ensure agile development and prototyping, as well as commercializing solutions.” Foremost may be the importance of investing in new people with the skills that can assist in this learning process. Obviously, it is not easy to convince a new generation that working in a traditional bank is ‘cool’.
PwC provides six strategies to solidify a firm’s approach to innovation:
- Focus on evaluating emerging technologies
- Consider a partnership for expedient innovation
- Replace legacy systems and integrate new technologies
- Embrace agile IT culture
- Understand the new digital consumer
- Foster a culture of innovation
It will be close to impossible for incumbent financial organizations to ‘go it alone’ given the speed of technological change and customer expectations. Even with the benefits of fintech partnering or acquisition, there are still challenges with legacy IT architecture, operational silos and an outdated leadership culture. To succeed, organizations will need to move quickly to embrace a future that will be significantly different than the past.