The banking ecosystem is in a state of transformation. New fintech entrants are coming into the marketplace regularly, while traditional providers are trying to adjust to the realities of digitalization, advanced technology and increasing consumer demands. Moving from a competitive perspective, traditional financial institutions and fintech firms now understand that collaboration may be the best path to long-term growth.
Understanding the opportunity and being able to take action on this opportunity are not the same thing, however. Between differing cultures, vastly different infrastructures and an ever changing compliance playing field, collaboration between banking and fintech is far from simple, derailing many proposed partnerships.
According to the World Fintech Report 2018 from Capgemini and LinkedIn, in collaboration with Efma, successful collaboration will heavily rely on traditional institutions’ ability to identify and assess whether candidates for partnership have the characteristics necessary for sustained success across four pillars:
- People
- Finance
- Business
- Technology
The success of Bank+Fintech collaboration rests with those organizations who can understand each other’s strength and weaknesses to improve the customer experience while also reducing operational costs. Potentially more important will be whether these collaborations can deliver the level of personalization, speed, contextuality, and seamless delivery to defend positions against the threat of the more pronounced competition that could come from the likes of Google, Amazon, Facebook and Apple (GAFA) or challenges from Alibaba and Tencent.
The good news is that infrastructure-based technology, enabled through the potential of open Application Programming Interfaces (APIs), is transforming the financial services industry. Combined with the ability to process and analyze increasing amounts of consumer data with machine learning, and the automation benefits of robotic process automation (RPA), chatbots, and Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT), there is greater potential for agility, efficiency, and accuracy.
Read More:
- Open Banking Provides Potential For Revenue Goldmine
- 4 Tech Trends That Will Massively Transform Banking
- Banks Must Adopt APIs for Business Lending or the Fintechs Will Win

The unfair advantage for financial brands.
Offering aggressive financial marketing strategies custom-built for leaders looking to redefine industry norms and establish market dominance.

The Financial Brand Forum Kicks Off May 20th
Explore the big ideas, new innovations and latest trends reshaping banking at The Financial Brand Forum. Will you be there? Don't get left behind.
Read More about The Financial Brand Forum Kicks Off May 20th
Legacy Financial Institutions Poorly Positioned for the Future
The World Fintech Report 2018 discusses the variety of pressures legacy financial services organizations are experiencing due to the impact of new competition:
- New business models: The emergence of fintech firms has included the emergence of new business models such as peer-to-peer (P2P) payments and lending, crowdsourced solutions, social network scoring models and other innovations impacting all sectors.
- Speed and Efficiency: For an industry that lived with batch processing and monthly updates, the speed and accessibility introduced by fintech firms put pressure on distribution, delivery and innovation. Real-time updates, proactive alerts and agile innovation are an integral part of an enhanced customer experience.
- Transparency: With a digital-first and consumer-centric value proposition, fintech firms have a significantly lower cost structure than traditional banking organizations. This allows most fintech firms to offer services at a much lower cost and to clearly show prices up-front.
- Personalization: Digital organizations are much better positioned to provide highly personalized and customized solutions similar to what is experienced with Amazon. Despite having access to a treasure trove of customer insights, the pressure is on legacy organizations to apply these insights for the benefit of the consumer in the form of personalized and contextualized solutions.
- Pressure on margins and fees: As mentioned, fintech firms have no legacy infrastructure, keeping costs down compared to fixed cost burdened banking organizations with branches and old back-office processes. The introduction of automation, AI and robotic process automation has further widened the gap in delivery costs.
- Predictive modeling: At the foundation of most fintech firms is the ability to use predictive and analytical tools that are far less prevalent at most legacy organizations. This allows fintech firms to target and personalize offerings and communications based on customer profile and behavior.
- Digital distribution: The rise of fintech firms has forced incumbents to re-evaluate product and service distribution. Leveraging the power and accessibility of ‘always-on’ digital devices, fintech firms emphasize the simplicity of design and power of contextuality that consumers are increasingly expecting.
- Access to unserved/underserved segments: With a lower cost structure, fintech firms can deliver convenient and
affordable services to market segments that are unprofitable for legacy banking organizations. - Operational efficiency: Beyond the cost benefits delivered by the digital technology used by fintech firms, a completely rethought operational back-office has resulted in streamlined delivery and product development that provides a significant competitive advantage. From mortgage loan applications delivered on mobile devices to one-touch P2P payments, fintech firms have changed the game around internal efficiency and external simplicity.
- Advanced data analytics: Advanced analytics, combined with a broader pool of data sources, have enabled fintech firms to test new risk management and underwriting models, which results in lower costs, expanded prospect pools and higher efficiency.
- Design-based thinking: Simple-to-follow user interfaces are making the customer journey quick, convenient, and seamless, while insights, driven by data-focused technologies, are making it relevant through personalized and contextualized offerings. The emergence of augmented and virtual reality solutions as well as biometric advances are being developed that are helping customers interact with their firms in innovative ways.
Read More: AI’s Real Impact on Banking: The Critical Importance of Human Skills

Rationale for Collaboration
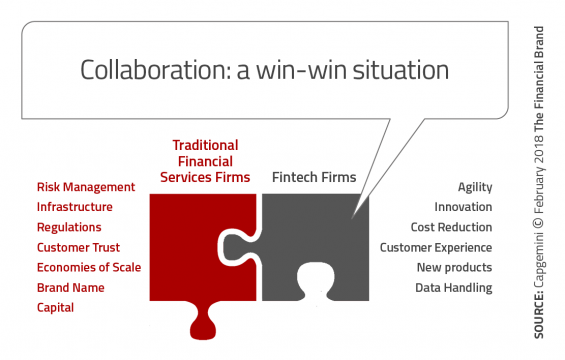
The rationale for any strong collaboration is the ability to bring a synergy of strengths together that create an entity stronger than either individual unit could bring on their own. For most fintech organizations, the primary differentiators are an innovation mindset, agility (speed to adjust), consumer-centric perspective and an infrastructure built for digital. These are obviously advantages that most legacy organizations don’t possess.
Alternatively, most fintech organizations lack the ability to scale adequately due to brand recognition and trust. They also usually lack capital, knowledge of compliance and regulations and an established distribution network. These are inherent strengths of traditional banking organizations.
According to the World Fintech Report, “Most successful fintech firms have focused on narrow functions or segments with high friction levels or those underserved by traditional financial institutions, but have struggled to profitably scale on their own. Traditional financial institutions have a vast customer base and deep pockets, but with legacy systems holding them back.”
As mentioned, the relationship between traditional banks and fintech firms has moved from competition to collaboration. The challenge is trying to cultivate an environment where collaboration can flourish as opposed to stifling the beneficiary attributes of either partner. One of the primary barriers mentioned in the CapGemini/LinkedIn report is the ability to find the talent required to facilitate these collaborations.
According to Bradley Leimer, Managing Director and Head of Fintech Strategy at Explorer Advisory & Capital, “Banks used to have truly well rounded financial relationships with their customers – but banks have now allowed the disintegration of customer-centric products and services and that’s where fintech solutions come in. Banks need to learn from and collaborate with the best fintech firms to ensure customer relevancy into the future.”

Positioning for the Future
The CapGemini/LinkedIn fintech report emphasizes the importance of focusing on customer needs as the foundation for building strong collaborations. Without this focus, there is the risk of ‘innovating for the sake of innovation’ without a true consumer purpose. While there is no surefire future-proofing strategy, there are some of the steps that the report believes will help minimize the threat of being left behind.
- Empathize with consumers
- Build and maintain consumer trust
- Keep it simple (for the consumer)
- Strive for operational excellence
- Invest in digital capabilities
- Align consumer and business goals
- Adapt agile principles
- Nurture the right culture and talent
Globally, more than 7,500 fintech firms, combined, have raised over $109.8 billion. The annual funding has grown exponentially from 2010 to 2016 ($5.1 billion to $28.4 billion). In 2017, fintech fundraising yielded $18.1 billion (up to end of
Q3).
Despite this commitment to the industry, the report states that most will likely fail because; they could not find the right product-market fit, the high cost of scaling up, inability to find the right partner, and the struggle to create, launch, and quickly gain market share for a differentiated product that cannot be replicated.
According to the report, “There is no one-size-fits all approach to successful collaboration because participants select from among various engagement models to best suit their strategic objectives. The most common engagement models are white labeling, in-house solutions, and leveraging APIs.”
The report also found that while some legacy organizations attempt to drive innovation from inside their organization, most work externally through incubators, accelerators, hackathons, and venture funds. The greatest concern from the perspective of fintech firms in working with traditional financial institutions is their lack of agility and struggle to move quickly.
According to Sonia Wedrychowicz, Managing Director, Head of Consumer Bank Technology for DBS Bank in Singapore, “The first rule is never incorporate a startup into the banking organization structure, as that will kill them. Second, is always look for complementary solutions that use progressive technologies that would take years to build yourself. Third, test it and experiment with it looking for relevance and customer adoption.”
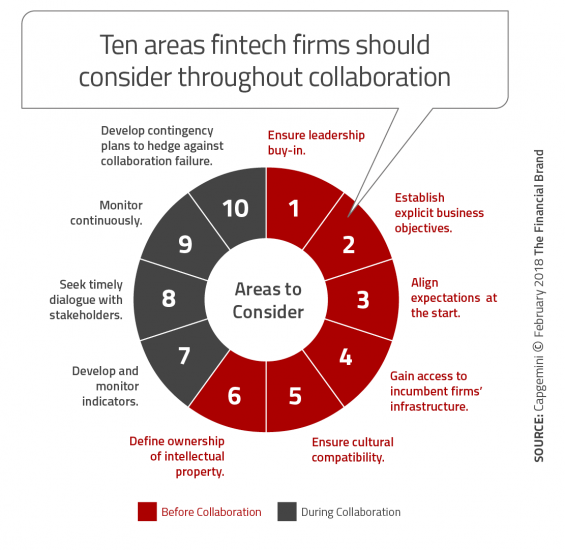
The report offered the following recommendations to help fintech firms to work more productively when partnering with
traditional financial services firms.
- Emphasis on agility: Fintech firms might face examples of native conservatism from incumbents. Therefore, fintech firms must spend extra time ensuring the legacy organization does not fall back into past habits.
- Leadership involvement: Regular and timely dialogue must be scheduled with senior innovation sponsors and stakeholders who are keen to ensure the firm supports the partnership.
- Proactive innovation: The innovation process must be continuous with the partnership investing ahead of the customer need.
- Cultural dynamics: Fintech firms and the partner incumbent should strive to create cultures that adapt to business and regulatory change. There must be flexibility and willingness to listen on both sides of the relationship.
- Regulatory responsibility: Fintech firms must keep up to date on compliance, regulations, and licensing information that could affect the collaboration.
- Governance and management: Managing the onboarding and integration of services requires a unified view by both the fintech and traditional firms, requiring a tight relationship between business and IT.
- Risk management: Care must be taken to be highly vigilant regarding data. Model risks and business resiliency also must be appropriately tested.
- Scaling the innovation: Determining and eliminating technological obstacles during the proof of concept or pilot phase will help to quickly scale the innovation. Continuously building and upgrading digital capabilities are also critical to sustaining and scaling the product and service innovation.
Even with the best collaboration, the ability for legacy and fintech organizations to compete in the banking ecosystem will most likely be challenged by the BigTech powerhouses such as Google, Amazon, Facebook and Apple as well as Alibaba and Tencent. Built on digital platforms, these huge organizations are efficient and have already found ways to reduce operational costs.
With a focus on using huge volumes of customer data to help predict behavior and improve the customer experience, BigTech firms could leverage customer trust and high engagement to introduce even more enhanced financial services. Add the potential to shift revenues from other businesses to enhance banking offerings and it is a brand new ballgame.