Over the past several years, the financial services industry began understanding the importance of digital transformation, as consumer expectations around digital engagement changed, competition from new digital-first organizations increased and the use of modern technologies became more commonplace. Despite knowing the need to move forward as more digitally adept organizations, most financial institutions still hesitated to invest in improved data management, analytics, modern technology, innovation and updated systems.
As COVID-19 took hold, comfort levels and willingness to engage digitally increased across all consumer segments and within all industries. The urgency for improved digital solutions forced organizations of all sizes to quickly implement digital transformation initiatives.
In research recently conducted by the Digital Banking Report, it was found that success with digital transformation initiatives has been hard to achieve. While organizations have moved forward with many strategies to improve digital engagement, most believe they have fallen further behind what the marketplace expects.
Read More:
- How to Avoid Digital Transformation Failures in Banking
- Digital Transformation Requires More Than Technology Upgrades
- Banking Must Bridge the Growing Digital Transformation Skills Gap

Are You Ready for a Digital Transformation?
Unlock the potential of your financial institution's digital future with Arriba Advisors. Chart a course for growth, value and superior customer experiences.

Move the Needle from Attrition to Acquisition
Vericast’s 2024 Financial TrendWatch explores seven of today’s most critical financial services trends to provide a complete view of the current loyalty landscape.
Read More about Move the Needle from Attrition to Acquisition
Importance High for Majority of Digital Transformation Strategies
When financial institution executives were asked about the importance of alternative digital transformation strategies, improving the overall customer experience was considered to be of high or very high importance by 88% of organizations. The importance of improving the customer experience was followed closely by the need to improve the use of data, AI and advanced analytics (76% rated high or very high).
Illustrating the perceived broad scope of digital transformation initiatives at most financial institutions, the majority of the other possible digital transformation strategies were each rated almost identically by financial institution executives in the Digital Banking Report research. Innovation agility, improving marketing and sales, improved efficiency, improved risk management and reducing costs were each rated high or very high by roughly six in ten executives.
It is a bit concerning that the need to change the existing business model and transforming legacy core systems were considered the least important strategies despite research that indicates these strategies are of significant importance for transformation success.
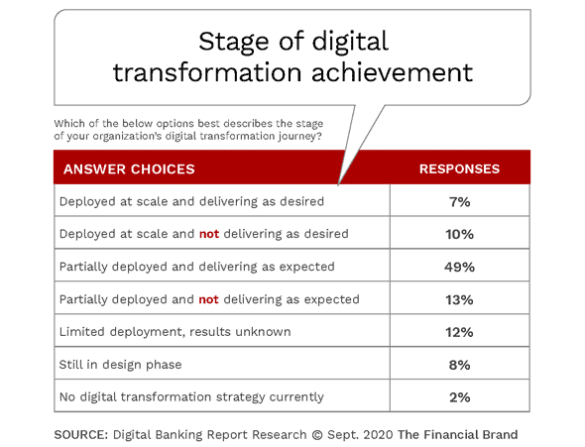
Progress Seen in Deployment of Digital Transformation
When asked about the progress of digital transformation efforts, only 17% of organizations surveyed indicated that the transformation was ‘deployed at scale’, which was the same level as in the 2019 research done by the Digital Banking Report. The good news is that 62% of organizations surveyed indicated that digital transformation was ‘partially deployed’ compared to only 41% last year. An additional 20% indicated that their efforts either had ‘limited deployment’ (12%) or were in the design phase (8%) compared to 27% and 11% respectively in 2019.
As was the case in 2019, the research found that there is a very strong correlation between ‘innovation pioneers’ and those firms where transformation was ‘deployed at scale’. This finding underscores that organizations where innovation is a priority are further ahead of peers in the desire to become a ‘digital bank’. These leader organizations also had top management support, were more committed to investing in the customer experience and advanced analytics, and were more likely to measure results of their efforts. Not surprisingly, these firms had more positive financial results than firms where digital transformation was only partially deployed.
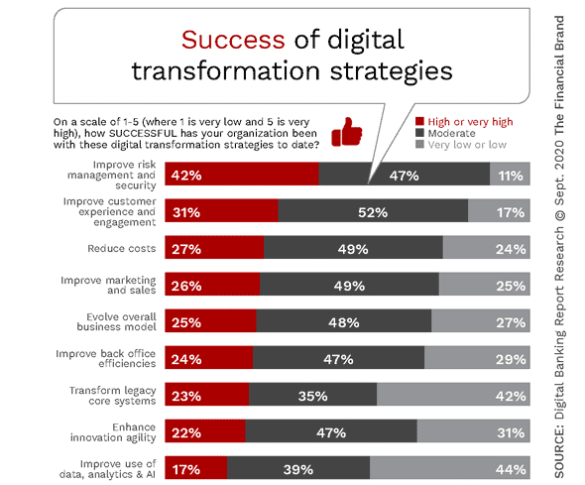
Success of Digital Transformation Still Lacking
It is clear that financial institutions understand the important components of successful digital banking transformation. From improving the customer experience to using data and advanced analytics for improved personalization, organizations are not lacking in the knowledge needed to know where to focus efforts.
Unfortunately, when organizations were asked about the success of their digital transformation strategies in meeting key objectives, results were far from encouraging. Potentially reflecting the reality that more than 6 in 10 institutions surveyed indicated that digital transformation efforts were only partially deployed, no digital transformation strategy had even half the organizations indicating that a strategy had high or very high success. Even then, the highest rated strategy was in risk and security – important, yet not consumer facing.
Of significant concern should be the finding that the lowest levels of success were found in the strategies of transforming legacy systems (23% high or very high success rating), enhancing innovation (22% high or very high rating), and improving the use of data and advanced analytics (17% high or very high rating). In fact, 44% of institutions stated that success in using data and analytics was low or very low.
Read More: What Makes A Great Digital Banking Transformation Leader?

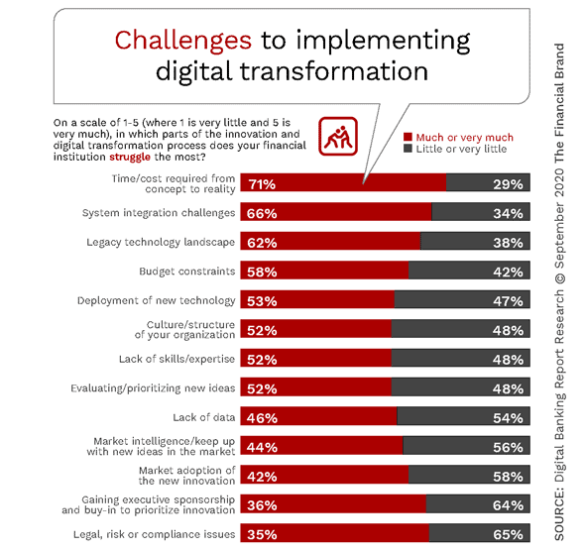
Top Digital Transformation Challenges
The top three challenge that banks and credit unions face in their digital banking transformation journeys are the time and cost of implementation (71%), systems integration (66%) and legacy technology (62%). These overarching issues were the top three challenges mentioned in the 2019 research by the Digital Banking Report, with legacy technology and systems integration both dropping by 10% in the number of organizations stating these were significant challenges.
The fourth most-cited challenge was budget constraints this year (58%) which was a similar level in 2019. The majority of the rest of the challenges had lower levels compared to 2019, with the challenges of culture and skills each dropping the most compared to last year (11% and 8% respectively) .
While this is encouraging, other research by the Digital Banking Report indicates that legacy cultures still must undergo a significant evolution to facilitate the digital transformation underway. While budgets are still very much in a state of flux for next year, the funding of digital transformation efforts must keep pace with needs. This is illustrated by the fact that budget constraints were mentioned by close to six out of ten organizations.
While progress seems to be occurring with the development of talent and skills throughout the organization, this is still a major challenge to digital transformation. This relates not just to specific capabilities, but also to the need for leaders who better understand how to integrate new digital methods and processes into existing ways of working. It is expected that this challenge will only get greater in the future due to the lack of experience in the marketplace.
As organizations take stock in the challenges faced with digital transformation, this list can provide guidance as to where emphasis should be placed.
Will COVID Inhibit or Enhance Digital Transformation?
The impact of COVID-19 could easily stall digital transformation if budgets are cut or skilled individuals are laid off due to financial challenges. However, the pandemic could also unlock hidden potential if commitment from top management is increased due to the realization that digital transformation is a competitive advantage to reach customers and maintain operational resilience.
The pandemic has also unlocked the potential to accelerate partnership discussions with fintechs and other ecosystem players. This can significantly speed up the digitalization of processes.
The questions will be whether organizations can maintain the focus and momentum that the pandemic put on digital transformation and whether the changes made will be permanent once the urgency of the current health crisis subsides.