The need for financial institutions to quickly operationalize their artificial intelligence capabilities has moved beyond important to imperative. More than supporting risk and fraud analysis, and increased productivity, a higher level of AI maturity at banks and credit unions will be a competitive differentiator, increasing business value across the organization.
The banking industry must move out of the formative stages of AI deployment to help enhance human intelligence. This includes uncovering the drivers of key performance measures such as revenue and profit, and propelling innovation in products, services, processes and customer service.
All financial institutions have the ability within reach to harness insights at scale – leveraging the right information, from the right people, at the right time. Instead of continuing to have people spend time and effort on tasks that can be better handled by computers, we need to use these computers (and AI) to enable humans to spend more time on the decisions that really matter.

Why Industry Cloud for Banking?
PwC’s Industry Cloud for Banking helps deliver personalized products and services that today’s customers expect.

The Financial Brand Forum Kicks Off May 20th
Explore the big ideas, new innovations and latest trends reshaping banking at The Financial Brand Forum. Will you be there? Don't get left behind.
Read More about The Financial Brand Forum Kicks Off May 20th
AI: Everywhere, Yet Nowhere
Although the concept of machines thinking like humans was discussed earlier, the field of AI research was founded in 1956 at a conference at Dartmouth College, where the term “artificial intelligence” was coined. While the attendees at this event agreed that AI was achievable, the following decades saw progress being slowed more by the power of computers as opposed to the imagination of researchers.
Today, we have vastly increasing amounts of data available, with computers and AI being used to collect and process this data into insight used in every industry, including financial services. Artificial intelligence has become embedded in our day-to-day existence, from smartphone voice assistants and mapping capabilities to computer intelligence that most of us take for granted.
AI is no longer a pipe dream.
AI Maturity Defined:
AI maturity measures the degree to which organizations have mastered AI-related capabilities in the right combination to achieve high performance for customers, shareholders and employees.
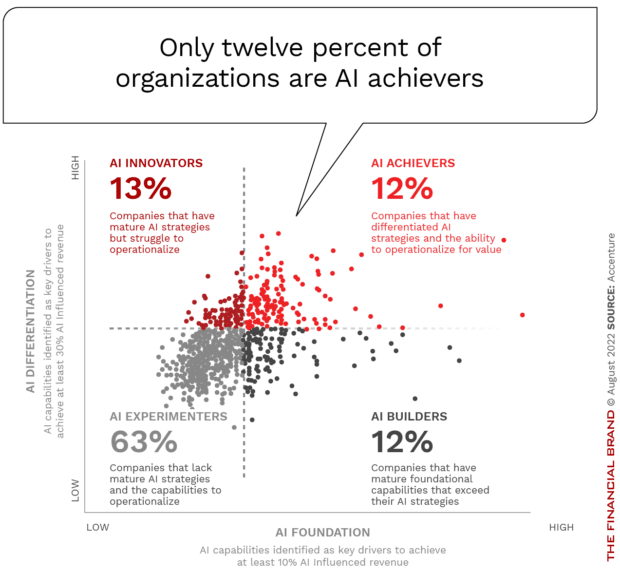
Yet, when it comes to making the most of AI’s full potential, most organizations in all industries are barely scratching the surface. According to research from Accenture, only 12% of all organizations have an AI maturity level high enough to achieve superior growth and business transformation (‘AI Achievers’). Another 25% of firms are somewhat advanced (‘Innovators’ or ‘Builders’), while the remaining 63% are still mostly testing the waters (‘AI Experimenters’).
The research found that AI maturity requires mastering a set of key capabilities including data and AI, but also organizational strategy, talent, and culture. Differentiation is achieved when AI capabilities are combined with C-suite sponsorship, revised business models and a culture of innovation supported by AI.
Read More:
- Artificial Intelligence in Banking: Top Priorities for 2022 (And Beyond)
- The Hidden Risks of Artificial Intelligence in Bank Marketing
- Three Practical Applications for Artificial Intelligence in Payments
Banking Industry Lacks AI Maturity
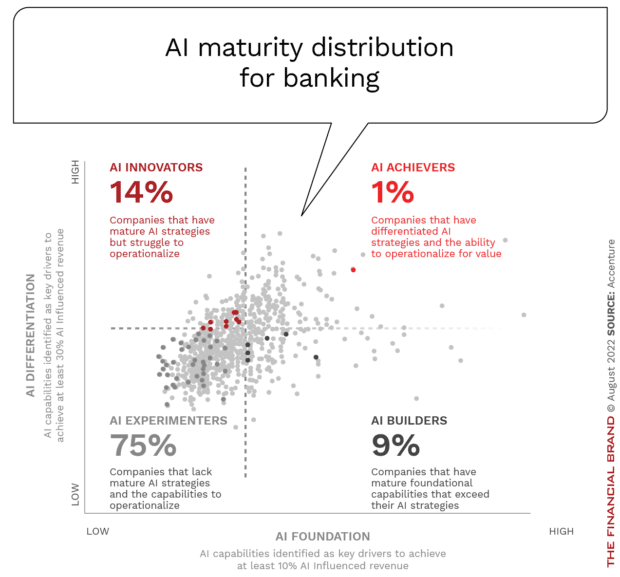
For financial institutions, the development and deployment of AI solutions is far less developed. According to Accenture, only 1% of financial institutions can be considered AI Achievers. More concerning is the reality that 75% of financial institutions are still in the early experimental stage of AI development. This is noteworthy, since Achievers, Builders and Innovators tend to devote more technology, time and talent to delivering on AI visions and to transform their organizations.
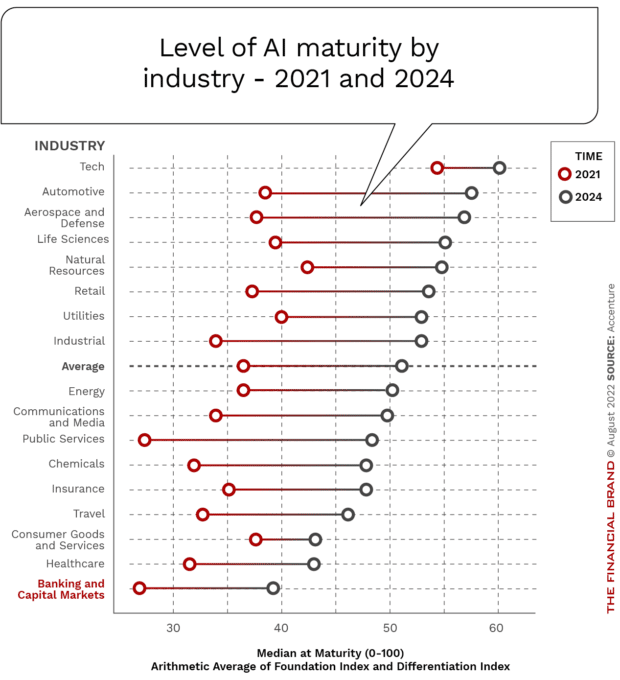
It may not be surprising that industries like technology are far ahead in their level AI maturity. What may be surprising is that financial services is at the bottom … by a relatively large margin. Even when estimates were made around the growth of AI maturity over the next few years, financial services remains at the bottom of industries evaluated.
That said, it is expected that the overall gap will narrow for financial services by 2024 despite some significant headwinds, such as legal and regulatory challenges, inadequate AI infrastructure, and a shortage of AI-trained workers. But, improvements must come quickly, since the machine learning models from Accenture show that the the most advanced ‘AI Achievers’ will more than double from the current 12% to 27% by 2024.

Why AI Maturity Matters
Creating AI use cases in finance must become a priority to drive competitive positioning and to prepare for a digital banking future. Research has found that investing in AI deployment not only can improve efficiencies, but can reduce the negative effects of economic pressures in the short term.
Accenture found that nearly 75% of companies have integrated AI into their business strategies and reworked their cloud plans to achieve AI success. For financial services, however, many of these initiatives are still in the formative stages. However, across all industries, nearly a third (30%) of AI pilot initiatives are improving back-office processes, accelerating R&D timelines for new products, and enhancing customer experiences.
“Of the most mature AI organizations, 42% said that the return on their AI initiatives exceeded their expectations, while only 1% said the return didn’t meet expectations,” according to Accenture. In addition, “the share of companies’ revenue that is ‘AI-influenced’ more than doubled between 2018 and 2021 and is expected to roughly triple between 2018 and 2024.”
4 Steps to Accelerate AI Success in Banking
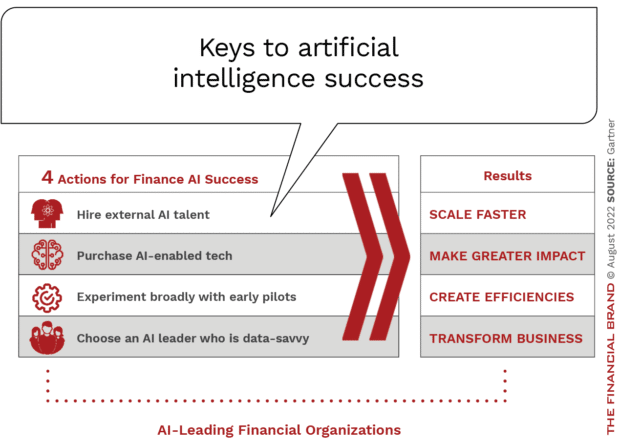
Gartner research shows that leading AI deployers share four common AI behaviors that enable them to quickly meet or exceed the expected impact of their AI projects and deliver critical finance and business outcomes.
- Hire External AI Talent. While up-skilling may be less expensive, there is a risk of slowing progress. New hired or partnered talent can more easily move beyond legacy thinking, bringing new ways to support AI deployment.
- Invest in Software With Embedded AI. Buying software with embedded AI functionality allows firms to experiment with AI and quickly build pilots for unique business challenges. According to Gartner, building in-house AI solutions can create more work and can reduces the bandwidth to explore new pilots or use cases.
- Experiment Early and Broadly. Taking a ‘fail fast’ approach to AI deployment allows for a wider array of pilots and a more rapid deployment of potential implementations. For financial institutions, slow and methodical processes can destroy momentum.
- Assign an AI Implementation Leader. AI must be seen as a strategic priority for the entire organization. Part of this commitment is to find an AI leader with both strong analytical and data backgrounds. This leader could have experience outside financial services, but must have an understanding of the complexities of AI in a business setting.
Become Future-Ready
The definition and requirements for being an AI-mature organization will evolve over time as will the technology itself. High performance AI organizations today will ultimately become business-as-usual tomorrow. “AI leaders have demonstrated that excellence in areas like vision and culture are just as critical as algorithmic integrity,” states Accenture.
As mentioned, AI Achievers are more likely to have formal senior sponsorship for their AI strategies. Accenture found that 83% of Achievers have such sponsorship, while only 67% of Builders and just 56% of Experimenters have it.
Finally, it is imperative for the building and deployment of AI to adhere to the laws, regulations and ethical norms. According to Accenture, “The ability to demonstrate high-quality, trustworthy AI systems that are ‘regulation ready’ will give first movers a significant advantage in the short- and long-term, enabling them to attract new customers, retain existing ones and build investor confidence.”